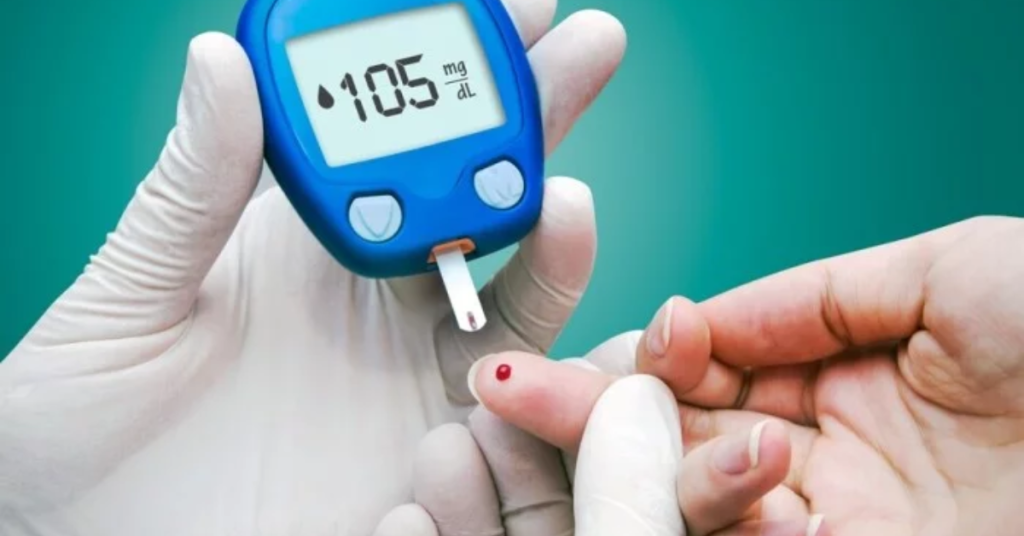
Diabetes is a group of diseases affecting how your body utilizes glucose. Glucose is important for overall health because it is a critical energy source for the cells in your tissues and muscles.
The cause of diabetes varies according to the type, but all can lead to excess blood sugar levels. When you have an excess of sugar in your blood, it can cause serious health problems. There are two chronic diabetes conditions, which are Type I diabetes and Type II diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
- Type I Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the immune system destroys the pancreas cells that produce insulin.
- Type II Diabetes: Occurs when cells become insulin resistant, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Prediabetes: A condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be considered diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and can be reversed once the baby is born.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetes?
The symptoms you experience depend on the level of your blood sugar. Some people may have few symptoms. With Type I diabetes, symptoms tend to develop quickly and are more severe. Some of the first signs of diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and the need to urinate more frequently
- Unexplained weight loss
- Experiencing extreme hunger
- Fatigue and irritability
- Frequent infections and slow-healing wounds
- Blurred vision
What Causes Diabetes?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas and secreted into the bloodstream. As insulin circulates, it allows sugar to enter body cells, reducing the amount of sugar in the bloodstream. As blood sugar levels decline, the pancreas produces less insulin.
- Type I Diabetes: Immune system destroys the pancreas cells producing insulin.
- Type II Diabetes and Prediabetes: Cells become insulin resistant, and the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy lead to increased insulin resistance.
Complications Caused by Diabetes
Long-term complications increase the longer you have diabetes and if your blood sugar levels aren’t well-controlled. These complications can include:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney damage
- Eye problems
- Neuropathy or nerve damage
Diabetes Tests
If a doctor suspects you have diabetes, they may perform blood tests, such as the A1C test, to determine your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
Diabetes Treatments
Managing diabetes includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Our physicians will help create a tailored plan for your treatment. Some treatments include:
- Neuropathy Treatment: Managing nerve pain caused by neuropathy with medications like antidepressants or antiseizure drugs.
- Type I Diabetes Treatment: Involves insulin pumps or injections with frequent blood sugar checks.
- Type II Diabetes Treatment: Focuses on lifestyle changes, blood sugar monitoring, and medications or insulin if needed.